
45 If a distribution has a mean of 25 and a standard deviation of 2, what value would be −4 standard deviations from the mean?ĭ. 130 If a distribution has a mean of 50 and a standard deviation of 5, what value would be −1 standard deviation from the mean?ĭ. 50% If a distribution has a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15, what value would be +2 standard deviations from the mean?ĭ. 68% _ of scores fall on either side of the distribution.ĭ. 99.5% _ of scores fall within one standard deviation of the mean.ĭ. 80 _ of scores fall within three standard deviations of the mean.ĭ. 40 What is the t score for a z score of +3?ĭ. −2.5 What is the t score for a z score of −1?ĭ. 3 A score that is 2.5 standard deviations below the mean would have a z score of _.ĭ. positive A score that is three standard deviations above the mean would have a z score of _.ĭ. negative z scores that fall above the mean are _.ĭ. the mean from the raw score and divide this difference by the standard deviation z scores that fall below the mean are _.ĭ. the raw score from the mean and divide this difference by the variance a. the raw score from the mean and divide this difference by the standard deviationĭ. the mean from the raw score and divide this difference by the varianceĬ. the mean from the raw score and divide this difference by the standard deviationī. z score To calculate a z score, you subtract _.Ī. 100% The _ is the most commonly used standard score.ĭ. 2.0 If the null hypothesis claims that there is no difference between groups, it assumes the likelihood of this to be _.ĭ. 5% What is the z score for a raw score of 85 where the group mean is 75, and the standard deviation is 5?ĭ. 2^10 Under the normal curve, if a z score of 1.65 included 45% of the area above the mean, what percentage would remain above 1.65 on the x-axis?ĭ.
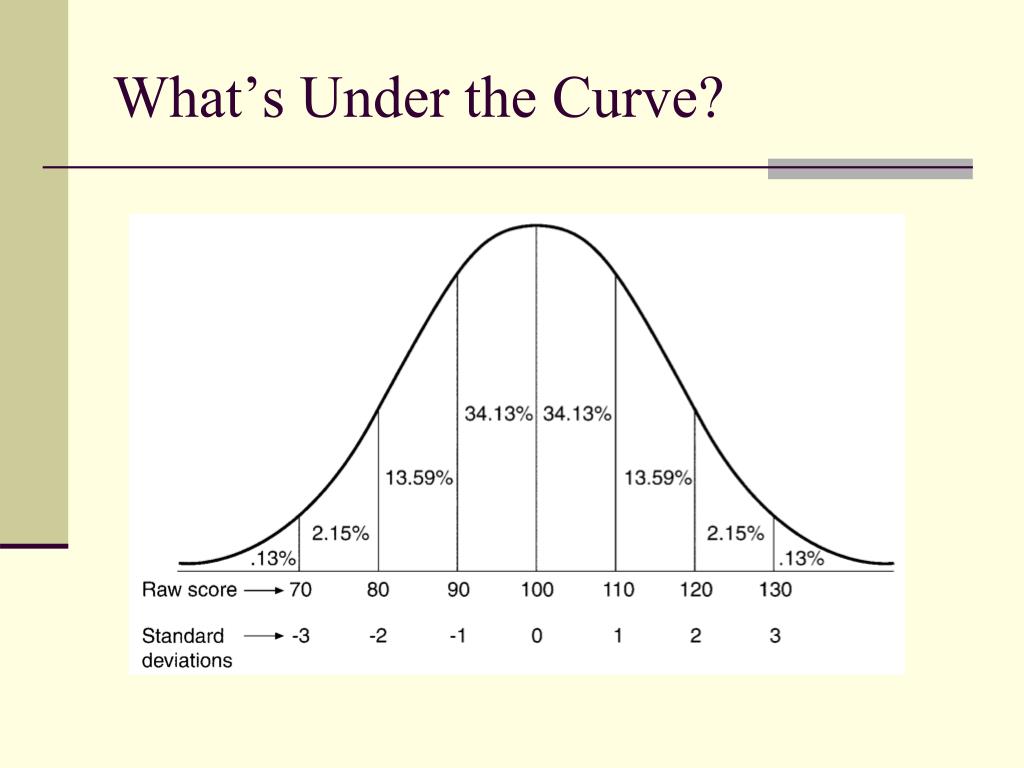
If I flip a coin 10 times, how many possible combinations or outcomes could I have?ĭ. t score What is the standard used by statisticians to determine the probability of an event occurring outside of chance alone?ĭ. 16% What type of standard score is computed by multiplying the z score by 10 and adding 50?ĭ. 16% In a distribution with a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15, what is the probability that a score will be 115 or higher?ĭ. 84% What percentage of all scores fall above a z score of +1?ĭ. What percentage of all scores fall below a z score of +1?ĭ. Values very close to the mean What is true of z scores that are equal to the mean?ĭ. What types of values are most likely to be seen?ĭ.
They are negative Which of the following is true of z scores that fall above the mean?ĭ. They are in the upper half of the distribution. X = z(s) + M Which of the following is true of z scores that fall below the mean?ĭ.

mean and standard deviation If you know the z score, standard deviation(s), and mean (M), what formula would you use to compute the raw score (X)?ĭ. z score If you want to calculate a z score for a test where your raw score was 24, what other information must you know?ĭ. 14% What type of standard score has M = 0 and SD = 1?ĭ. Under the normal curve, approximately what percentage of scores falls between −1 and −2 standard deviations below the mean?ĭ.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
